A New Analytical Service from Reach Separations: EPSA
In order for an oral drug to be efficacious it needs to have good absorption.
The first challenge in achieving this is getting the drug across the lipid bilayer membrane – as such, a method of determining this permeability is required as part of any design – make – test cycle.
Classically permeability has been measured via in situ perfusion through isolated intestinal segments, ex vivo diffusion across tissues or more commonly by in vitro permeation through cell monolayers (Caco-2), however these methods do not provide robust and consistent results for a variety of non-classical drug candidates, such as PROTACs or cyclic peptides.
In 2014, Goetz et al(1), introduced a supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) based methodology to provide experimental results that could be directly related to permeability.
Experimental Polar Surface Area (EPSA) is an experimental value that can be calculated based on the retention time of an analyte on a system calibrated using compounds of known EPSA values.
Always keen to harness the benefits of SFC to better support our clients in drug discovery, Reach has implemented this high throughput method to measure a compound’s polar surface area, a significant factor in its permeability.
Both of our sites, in Nottingham and Strasbourg now offer the EPSA assay.
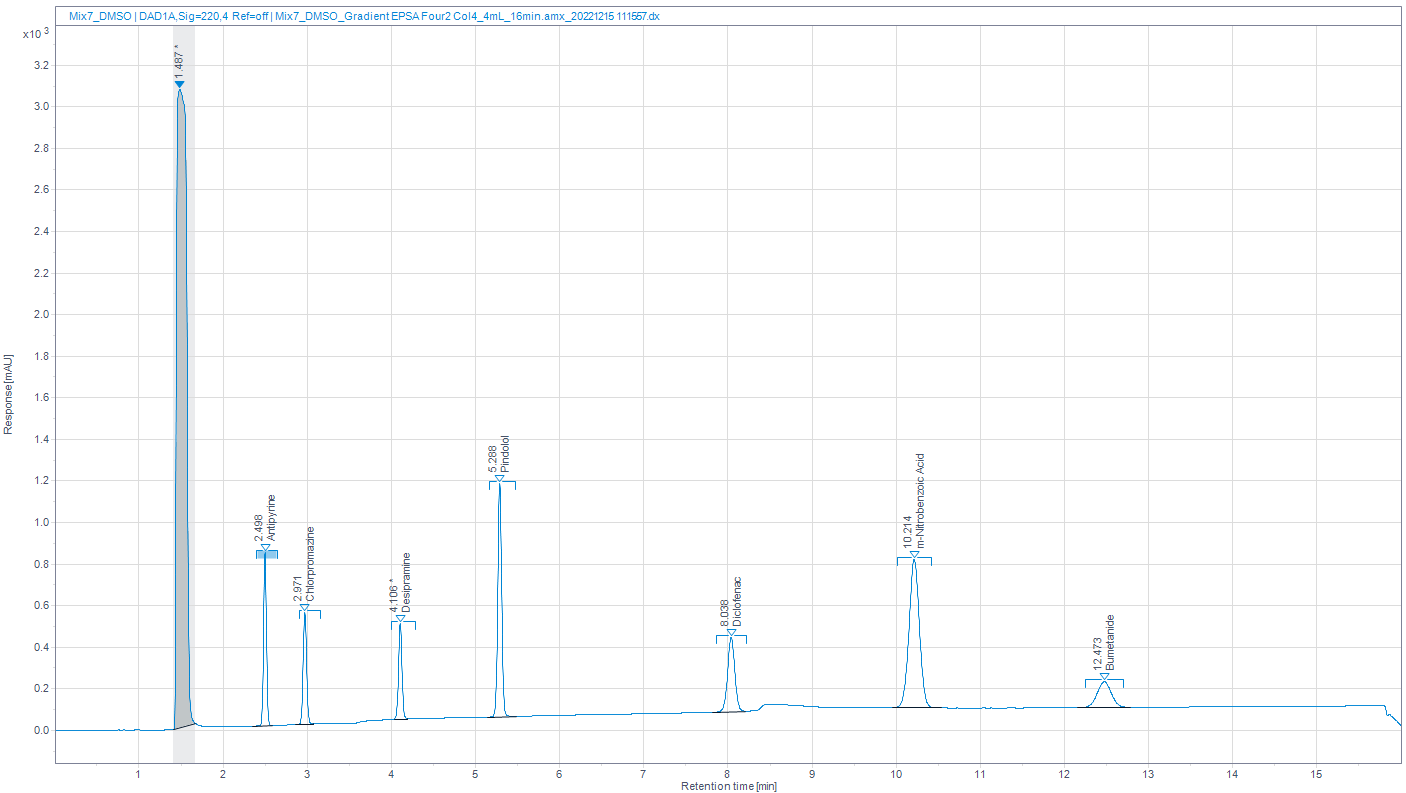
To ensure robustness of our results, the calibration was performed again multiple times across three days, ensuring fresh preparation of solvents and standards in each case, the calibration curve below shows the reliability of both the instrumentation and the data and we are confident that we can provide reliable data quickly and efficiently.
Would EPSA data benefit your project, please get in touch to find out more. You can download our white paper on EPSA here